Structuring Family Offices: Leveraging Organizational Clarity for Optimal Management
Introduction
Family offices play a crucial role in managing the wealth of high-net-worth families, handling everything from investments to estate planning. In this article, we'll explore the importance of structuring family offices effectively, ensuring they run smoothly and meet their legal and financial obligations.
Defining Family Offices
Family offices are private firms dedicated to managing the financial and personal affairs of affluent families. They provide a range of services, including investment management, estate planning, and comprehensive financial services, tailored to meet the unique needs of each family.
Proper structuring of family offices is essential for maximizing tax benefits, seizing new investment opportunities, protecting assets, and ensuring smooth succession to younger generations. This strategic foundation not only meets legal requirements but also drives long-term wealth preservation and growth.
Benefits of Family Offices
Personalized Financial Management
Family offices provide bespoke financial management tailored to each family's unique needs. For instance, a family office might help a family diversify their portfolio by investing in emerging markets, aligning with their risk tolerance and growth objectives. This personalized approach ensures that financial strategies are closely aligned with the family's long-term goals and values.
Tailored Investment Strategies
Investment strategies crafted by family offices are designed to meet the specific goals of the family. For example, a family interested in sustainable investments could have their family office focus on acquiring green bonds and investing in renewable energy projects. By tailoring investment strategies, family offices help families achieve their financial goals while adhering to their personal values.
Tax Optimization
Effective tax planning is a cornerstone of family office services. A family office might structure investments through tax-efficient vehicles like trusts or limited liability companies (LLCs) to minimize tax liabilities. For instance, by setting up a trust, a family can protect their wealth from hefty estate taxes, ensuring more of their assets are preserved for future generations.
Estate Planning and Succession
Family offices excel in planning for the transfer of wealth across generations. They create detailed estate plans that outline the distribution of assets, aiming to avoid conflicts and ensure smooth transitions. A family office might help a family establish a family governance structure, complete with a charter that outlines the roles and responsibilities of each family member in managing the family business.
Long-Term Wealth Preservation
Preserving wealth over the long term requires a strategic approach. Family offices employ strategies like diversifying investments, managing risks, and planning for future generations. For example, they might advise investing in a mix of real estate, equities, and private equity to spread risk and achieve steady growth. This approach ensures the family's wealth remains intact and continues to grow, securing their financial future.
Types of Family Offices
Understanding the different types of family offices helps in choosing the right structure for your needs. Each type offers distinct advantages tailored to specific family dynamics and financial goals.
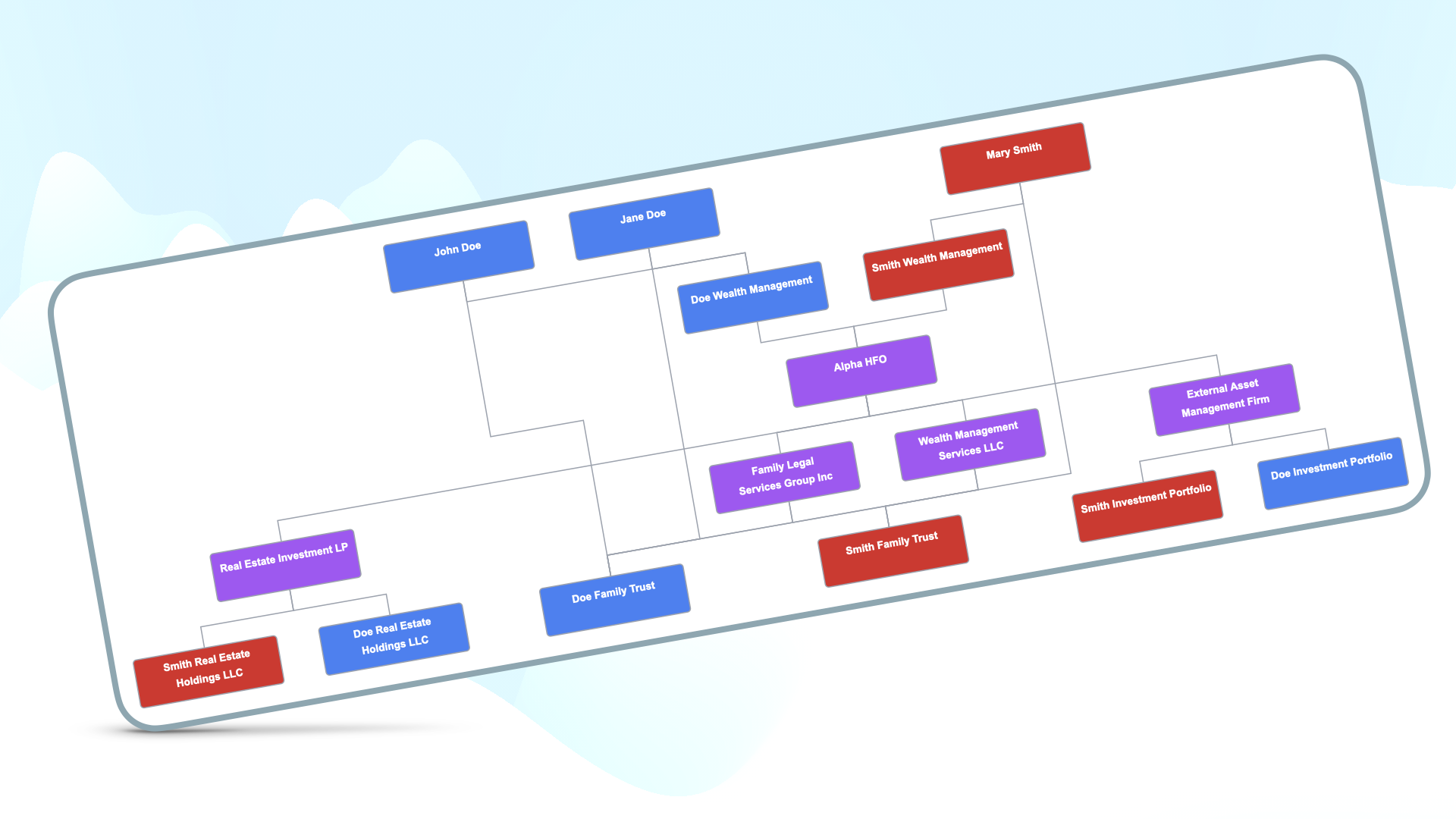
Single Family Office Structure
Single family offices cater exclusively to one family's financial and administrative needs. Picture a streamlined operation, focused solely on preserving and growing a single family's wealth.
Family Council
At the top sits the family council or board of directors. Composed of family members, this group sets strategic directions, oversees major decisions, and ensures that the family's values and goals are upheld. They meet regularly to discuss long-term plans, investment strategies, and succession planning.
Single Family Office Executive Team
Beneath the family council is the executive team, led by a CEO. This team handles the daily operations and ensures the office runs smoothly. Key positions include a Chief Investment Officer (CIO), Chief Legal Officer (CLO), and Chief Financial Officer (CFO), each overseeing their respective domains.
Specialized Departments
- Investment Department: Manages the family's investment portfolio, conducts market research, and makes investment decisions aimed at growth and preservation.
- Legal Department: Handles all legal matters, ensuring compliance with regulations and managing legal risks.
- Tax Department: Focuses on tax planning and compliance, working to minimize tax liabilities and optimize tax benefits.
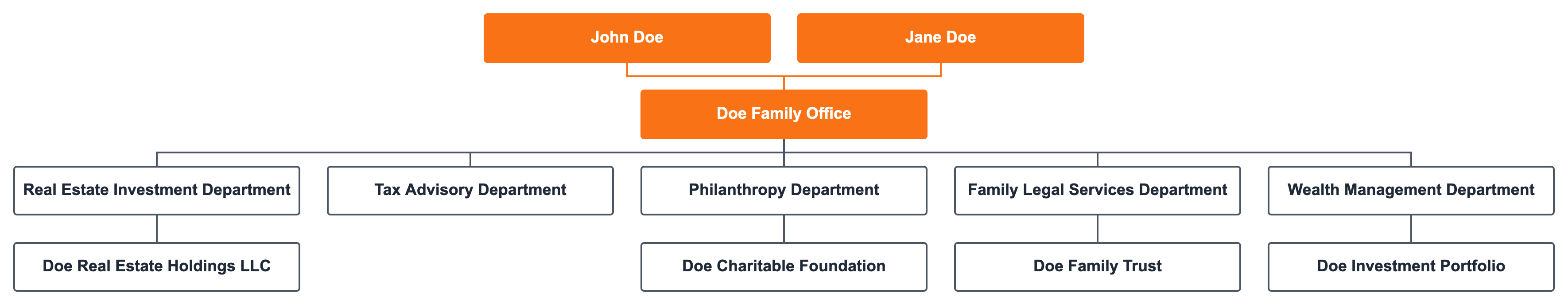
Multi-Family Office Structure
Multi-family offices pool resources to serve multiple families, offering a broad array of services at a reduced cost. This setup is ideal for families seeking top-tier financial expertise without the expense of a dedicated office.
Advisory Boards
Each family has its own advisory board to ensure their specific needs and interests are met. These boards participate in decision-making processes and provide oversight for their family's assets and strategies.
Multi-Family Office Executive Team
A shared executive team manages overall operations. This team includes a CEO, CIO, CLO, and CFO, who coordinate the services provided to all families. They ensure that the multi-family office operates efficiently and that each family receives personalized attention.
Shared Specialized Departments
- Investment Department: Manages combined investment portfolios, offering diversified opportunities and leveraging economies of scale.
- Legal Department: Navigates complex regulatory environments and provides legal advice tailored to each family's needs.
- Tax Department: Develops tax strategies that optimize benefits for all families, ensuring compliance and minimizing liabilities.
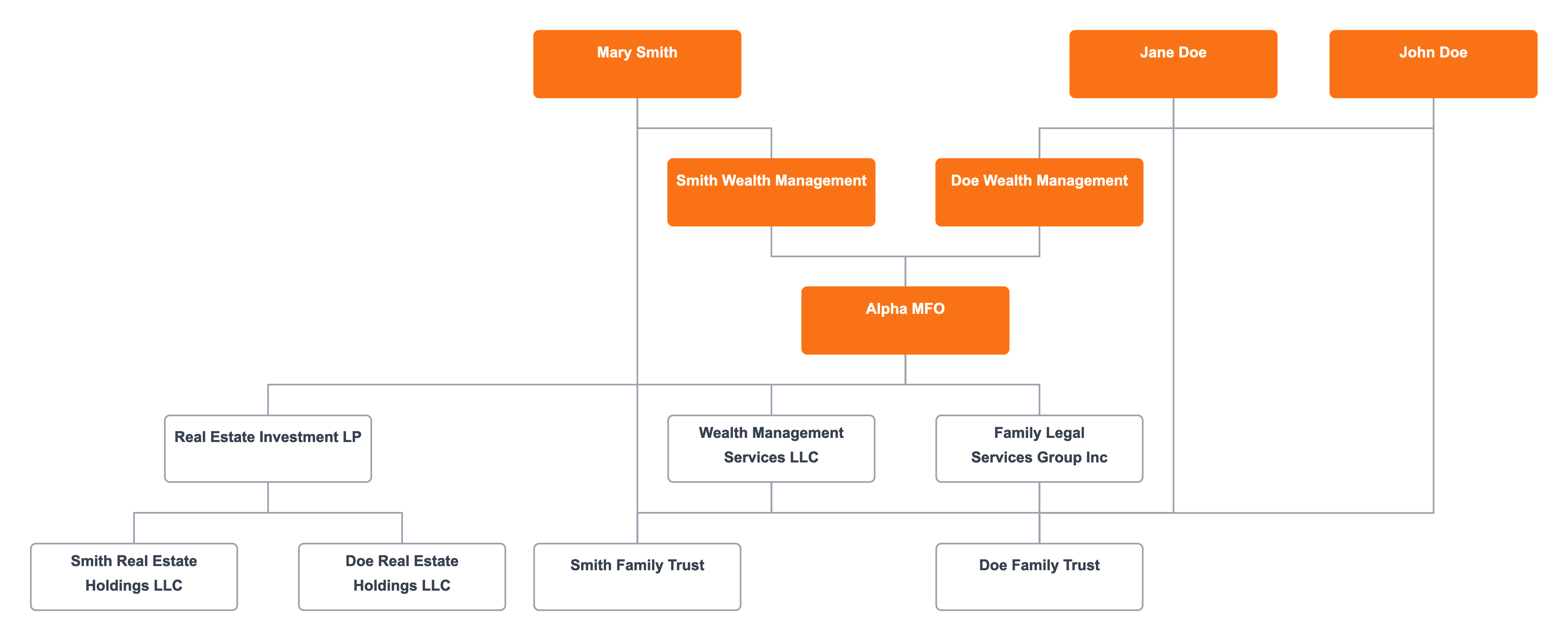
Hybrid Family Office Structure
Hybrid family offices blend the best of both single and multi-family models. They primarily serve one family while extending services to others on a selective basis, combining personalized attention with resource efficiency.
Primary Family Council
The primary family's council oversees the strategic direction and major decisions, ensuring their needs remain the top priority. This council works closely with the executive team to align the office's operations with their goals.
Hybrid Family Office Executive Team
The executive team, led by a CEO, manages both the primary family's affairs and the additional families they serve. This team must balance the personalized service expected by the primary family with the efficient management required for serving others.
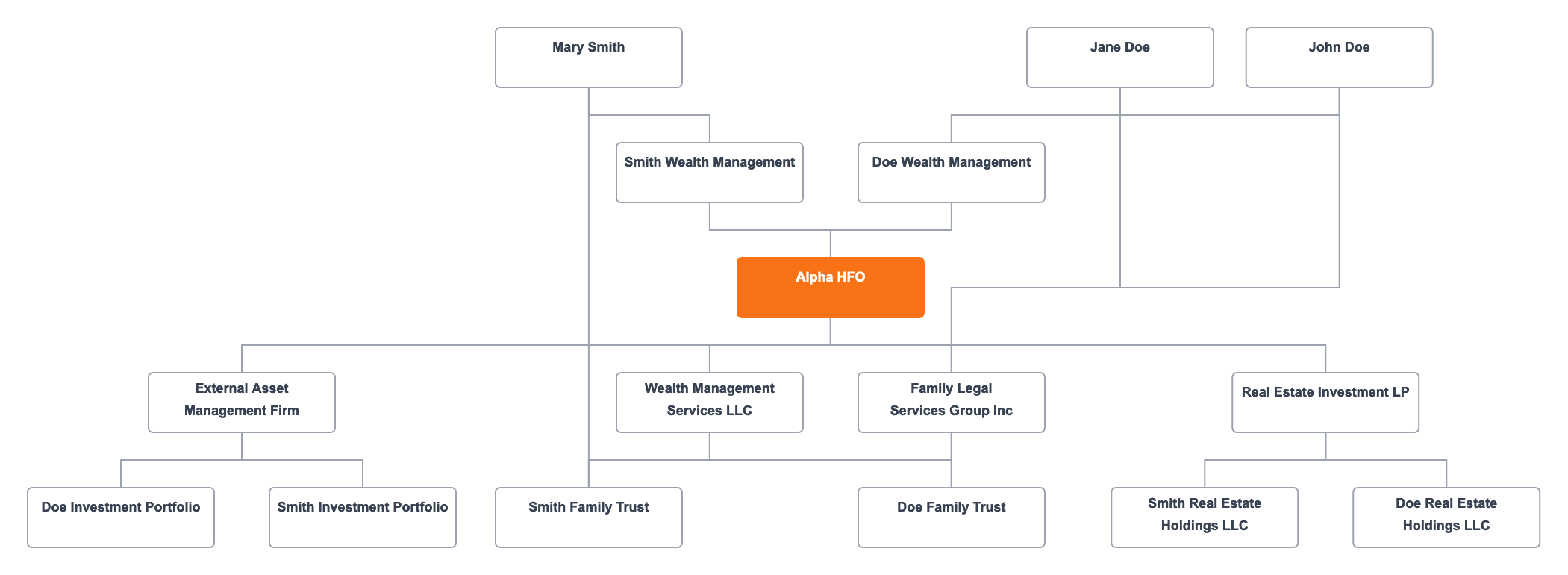
Departments Handling Shared Services
- Investment Department: Offers tailored investment strategies to meet the varying risk appetites and goals of each family, managing a diverse portfolio of assets.
- Legal Department: Provides customized legal advice and ensures compliance with multi-jurisdictional regulations.
- Tax Department: Focuses on tax planning and compliance, optimizing tax outcomes for both the primary and secondary families.
Hybrid family offices must remain flexible, scaling services up or down based on the needs of the families they serve. This adaptability ensures that all families receive high-quality service and that the primary family's priorities are always met.
Key Elements of Family Office Structure
Organizational Hierarchy
Clear hierarchical structures are vital in family offices. At the top is the family council or board of directors, setting the strategic direction and making high-level decisions. Below them is the executive team, responsible for daily management and overseeing specialized departments such as investment, legal, and tax. This clarity in roles enhances accountability and efficiency.
Legal and Tax Structures
Family offices use various legal entities, such as trusts, limited liability companies (LLCs), and corporations. Trusts manage and protect wealth, LLCs offer flexibility and liability protection, and corporations provide different tax advantages. Choosing the right entity depends on the family's goals and assets, ensuring compliance and optimal tax outcomes.
Investment Structures
Investing in businesses and other assets requires clear structures to manage risks and clarify ownership. Family offices often use holding companies or special purpose vehicles (SPVs) to isolate risks and manage investments. Diversifying the investment portfolio across different asset classes helps balance risks and achieve consistent returns.
Creating a Family Office Structure
Launching a family office starts with a clear vision and a solid plan. Think of it as building a ship for a long voyage. First, you need to chart the course. Define your family's objectives: Are you focused on growing your wealth, preserving it, or perhaps giving back through philanthropy? This vision sets the foundation.
Defining Objectives
Identify what matters most to your family. Is it investment growth, legacy planning, or tax efficiency? For instance, a family might prioritize establishing a philanthropic foundation to support education. These goals will shape the structure and services of your family office.
Key Roles and Recruitment
Assemble a team of experts. Imagine drafting your own dream team: a savvy CEO, a sharp CFO, an astute CIO, and seasoned legal and tax advisors. These professionals are crucial in steering your family office towards its goals. For example, hiring a CIO with experience in sustainable investments can align with a family's interest in green initiatives.
Establishing the Legal Framework
Choose the right legal entities to protect and grow your assets. This might include setting up trusts for estate planning or creating LLCs for liability protection. For instance, a trust can ensure your wealth passes seamlessly to the next generation while minimizing estate taxes.
Creating the Organizational Chart
Draw an organizational chart that maps out roles and responsibilities clearly. This blueprint helps everyone understand their place and function within the family office. It’s like having a detailed map before setting sail, ensuring that every team member knows their role in achieving the family’s vision.

Maintaining and Adapting Structures
Building a family office is just the beginning. Keeping it running smoothly requires ongoing attention and flexibility, much like maintaining a ship on its journey.
Regular Performance Reviews
Conduct regular reviews to assess how well the family office is meeting its objectives. Are investments performing as expected? Is the tax strategy delivering the anticipated benefits? For example, a quarterly review might reveal that a particular investment isn’t yielding the desired returns, prompting a strategic pivot.
Adapting to Changing Needs
Families evolve, and so should their family office. Whether it’s adapting to new regulatory landscapes or shifting family dynamics, flexibility is key. Imagine a family expanding its business operations globally; the family office might need to establish new legal entities in different countries to manage international investments.
Ensuring Compliance
Stay ahead of regulatory changes to avoid legal pitfalls. Regularly consult with legal and tax advisors to ensure the family office remains compliant with evolving laws. This proactive approach prevents costly mistakes and keeps the family’s assets secure.
By continuously refining its structure and operations, a family office can navigate the complexities of wealth management, ensuring that the family’s goals are met and its legacy is preserved for future generations.
Conclusion
Effective family office structures enhance efficiency, compliance, and decision-making. As family offices grow and evolve, the need for clear, adaptable structures becomes even more critical. Implementing detailed organizational charts and maintaining flexibility ensures the family office can meet its long-term goals and support the family's success.
This chart is made with Lexchart for automatic organization charts.


