Functional organization structure
There are several types of organizational structure within the category of a hierarchy chart. The most common types of organizational hierarchy are:
- Functional,
- Flat,
- Division, and
- Team.
This article focuses on the functional organizational structure.
Functional organizational structure defined
What is a functional organizational structure?
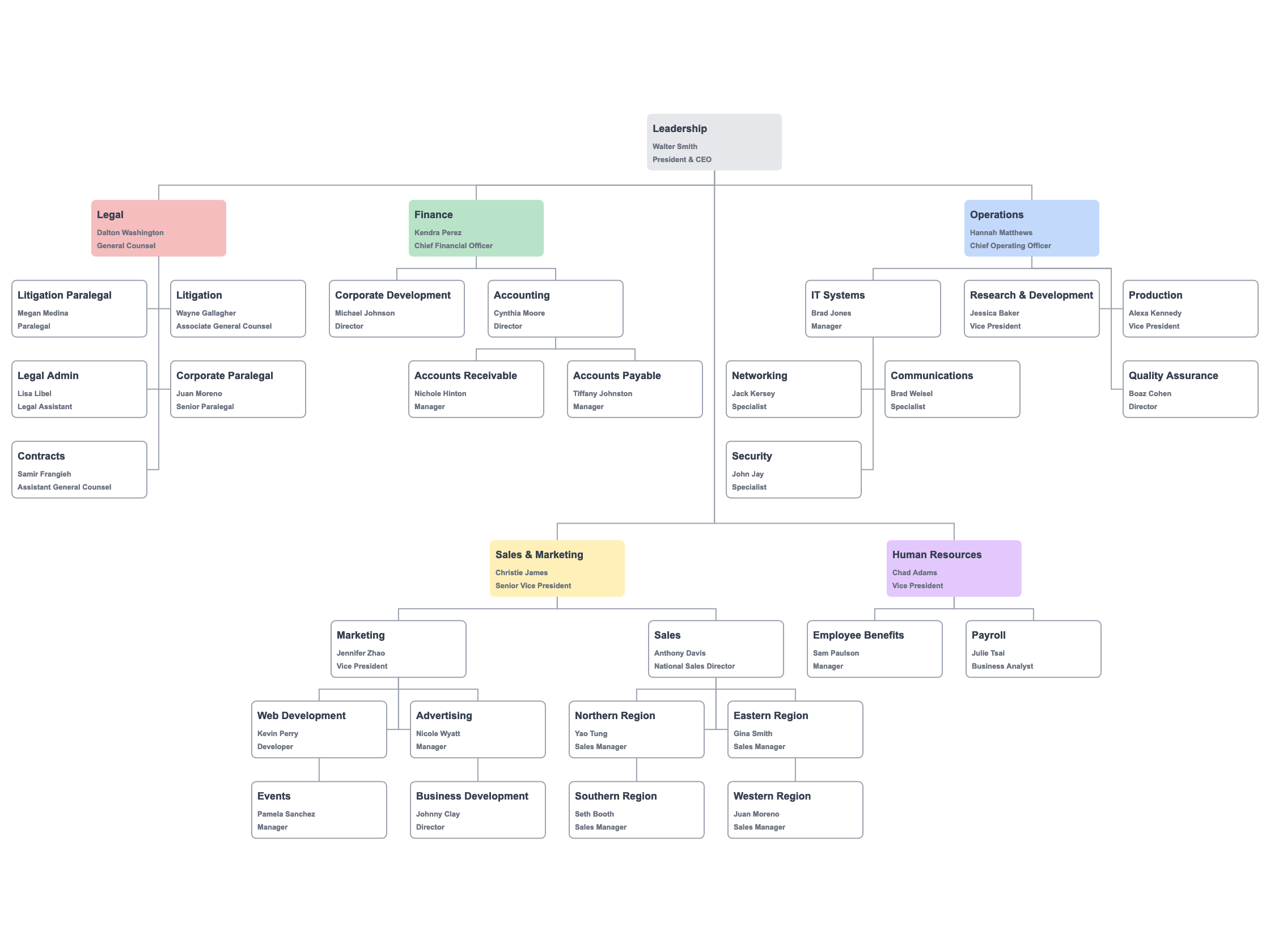
A functional organizational chart shows the reporting relationships among the business functions or departments. The chart is hierarchical. Senior management are listed at the top. The reporting structure flows down to staff.
A functional organization structure prioritizes the type of work in management reporting. A functional organization chart typically shows departments reporting to a top level executive or manager.1
Use the free org chart template for functional organization structures.
5 benefits of a functional org chart
There are 5 benefits of a functional organization chart:
- A functional org chart is clear
- A functional org chart identifies who is responsible for what
- A functional org chart show the span of authority
- A functional org chart is scalable
- A functional org chart shows expertise
Clarity
Businesses have organized themselves by department or function for a long time and across industries. As a traditional structure, these charts are easy to read with familiar disciples.
Consider the same organizational structure: one version presented as a pure hierarchy; the other as a functional structure.
This chart shows names and titles with reporting relationships.
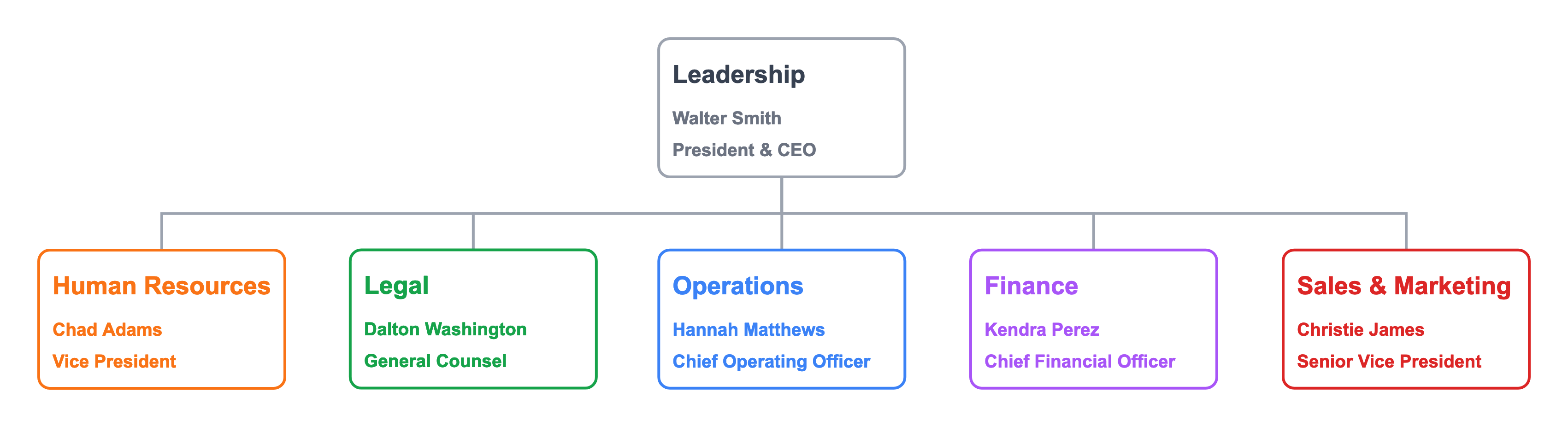
While this chart leads with the functional structure.
Names, titles, and reporting relationships are in the chart. The functional org chart offers more clarity.
Responsibility
The person or role at the top of any branch is the one responsible for the actions of the branch.
Titles can convey who has responsibility, but titles can be ambiguous.
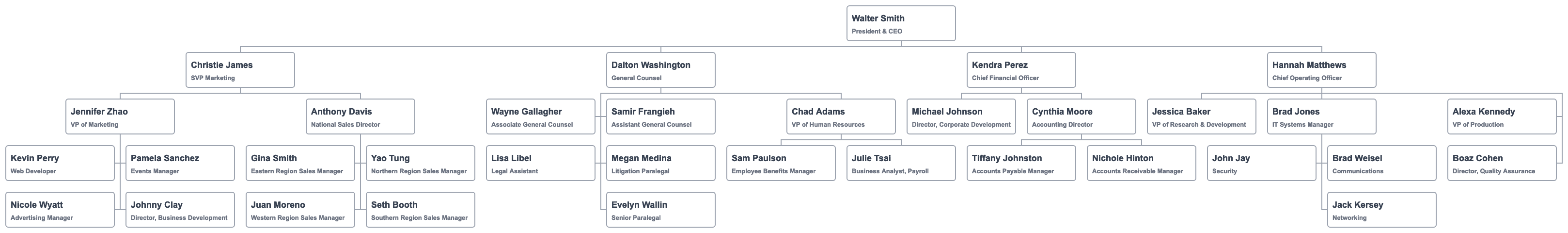
To illustrate, let's look at two employees: Johnny Clay and Michael Johnson. They share two traits. Both are "Directors". Neither has any direct reports. There must be something special about their roles to have a director title, but no direct reports?
To a chart reader unfamiliar with all the roles, Johnny and Michael have similar titles: "Business Development" and "Corporate Development." What is the difference?
Here is the hierarchy chart with Johnny and Michael's respective management structure.
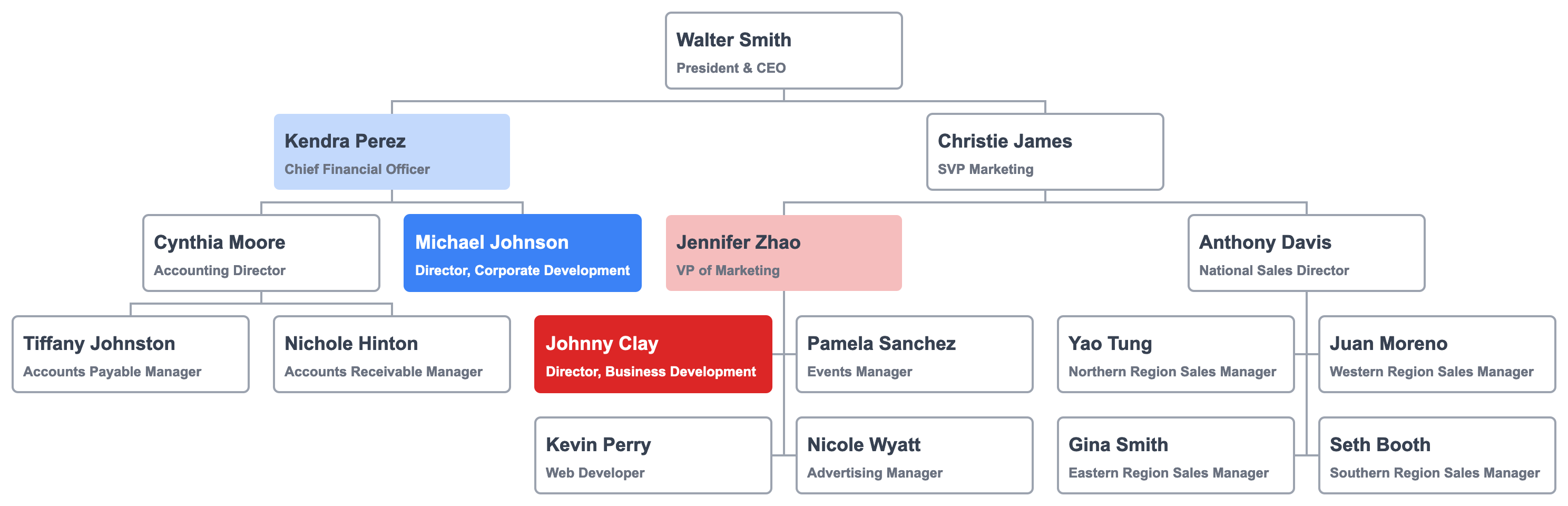
The only explicit information from that chart is that Michael reports to Kendra Perez and Johnny to Jennifer Zhao.
The functional org chart explicitly sets the context for all subordinate role.
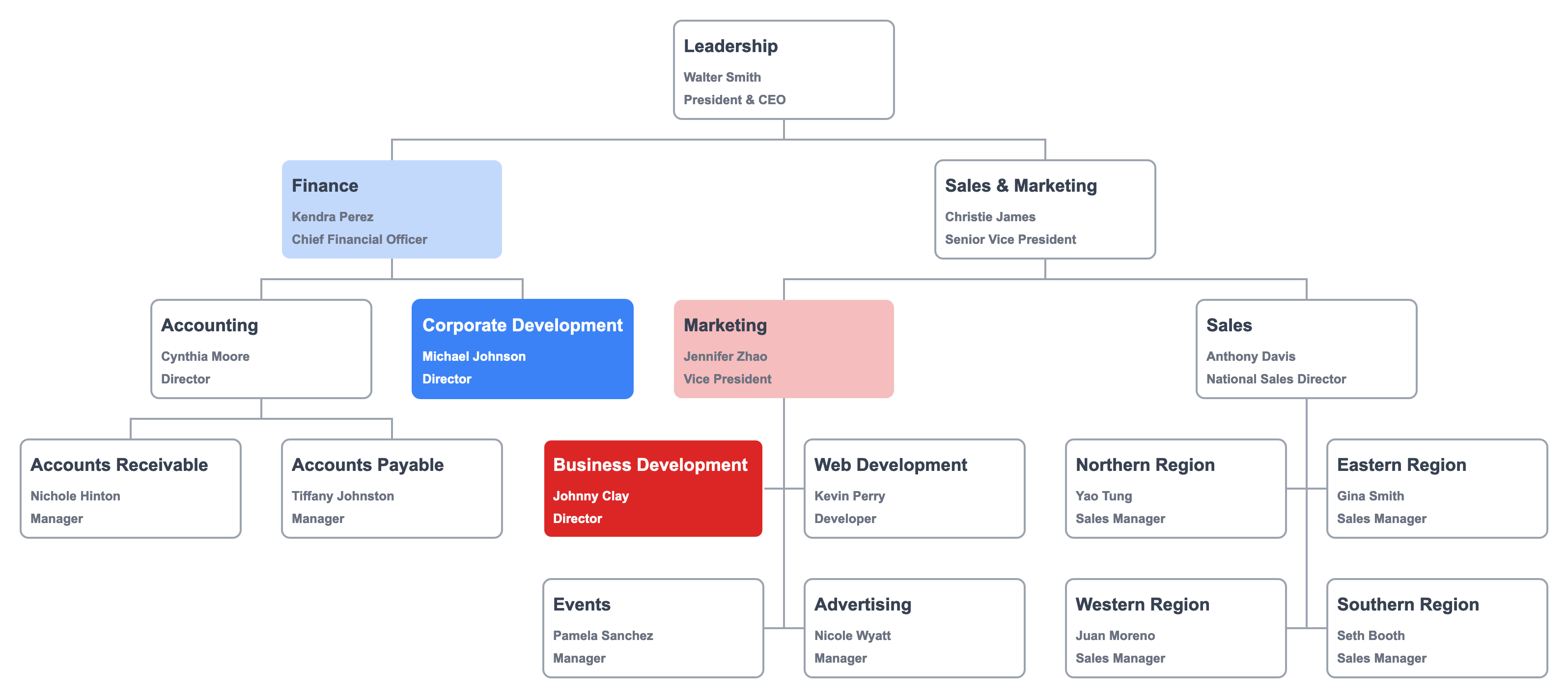
Now we know that Corporate Development is a Finance function. While Business Development is a Marketing function.
Authority
In the best organizations, responsibility and authority are paired. The person or role at the top of any branch is the one with authority to assign, review, and compensate work of people in the structure below.
A functional org chart conveys both the span of authority of the role and the responsible person.
Scale
Creating a functional org chart can extend to any layer of the organization.
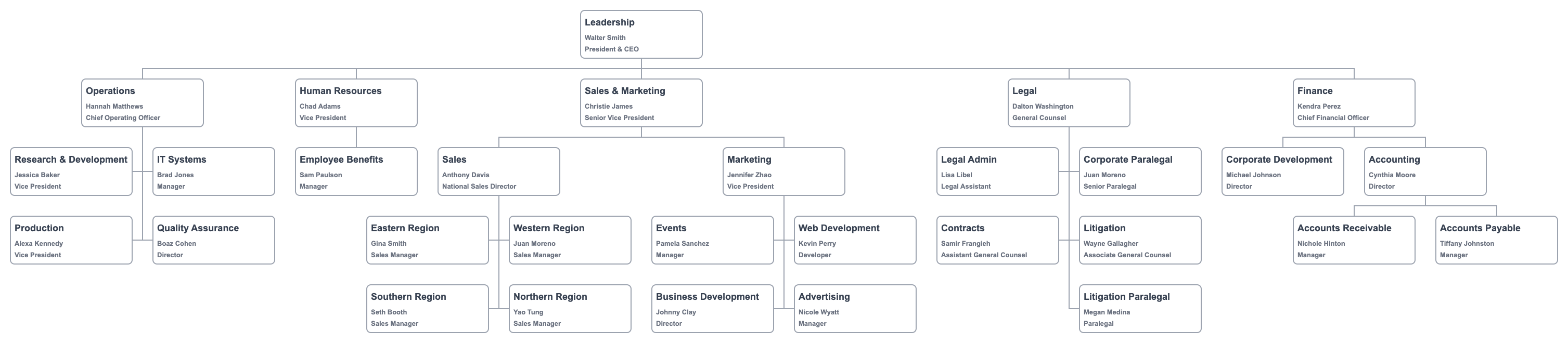
People are organized by the type of work required by the position.
Expertise
A functional org chat identifies expertise or competencies by job duty. Contrary to popular opinion, this can promote cross-functional collaboration, because it is easy for team leaders to spot experts across the organization who might be able to help with a particular problem or issue.
While not unique to functional charts, you can extend the data for each employee to elaborate of skills or expertise.
Department organization structure
Departments org chart
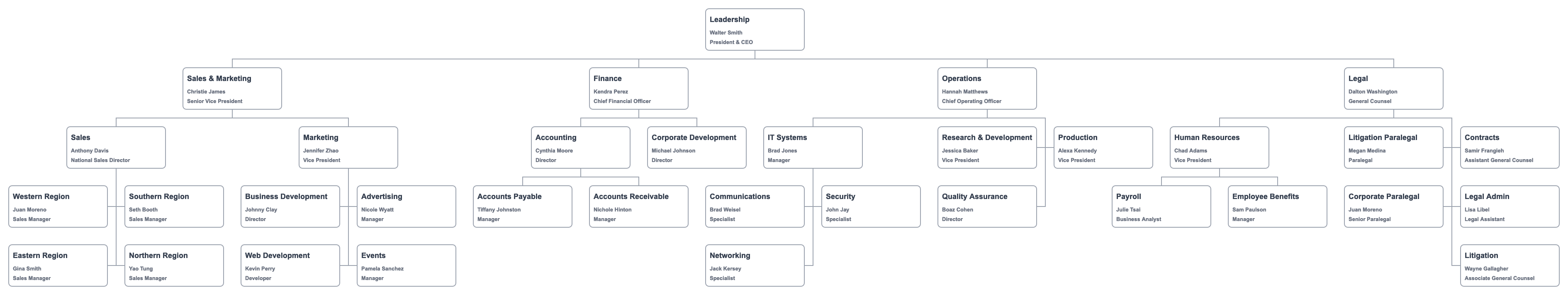
Department structures start with a collection of departments.
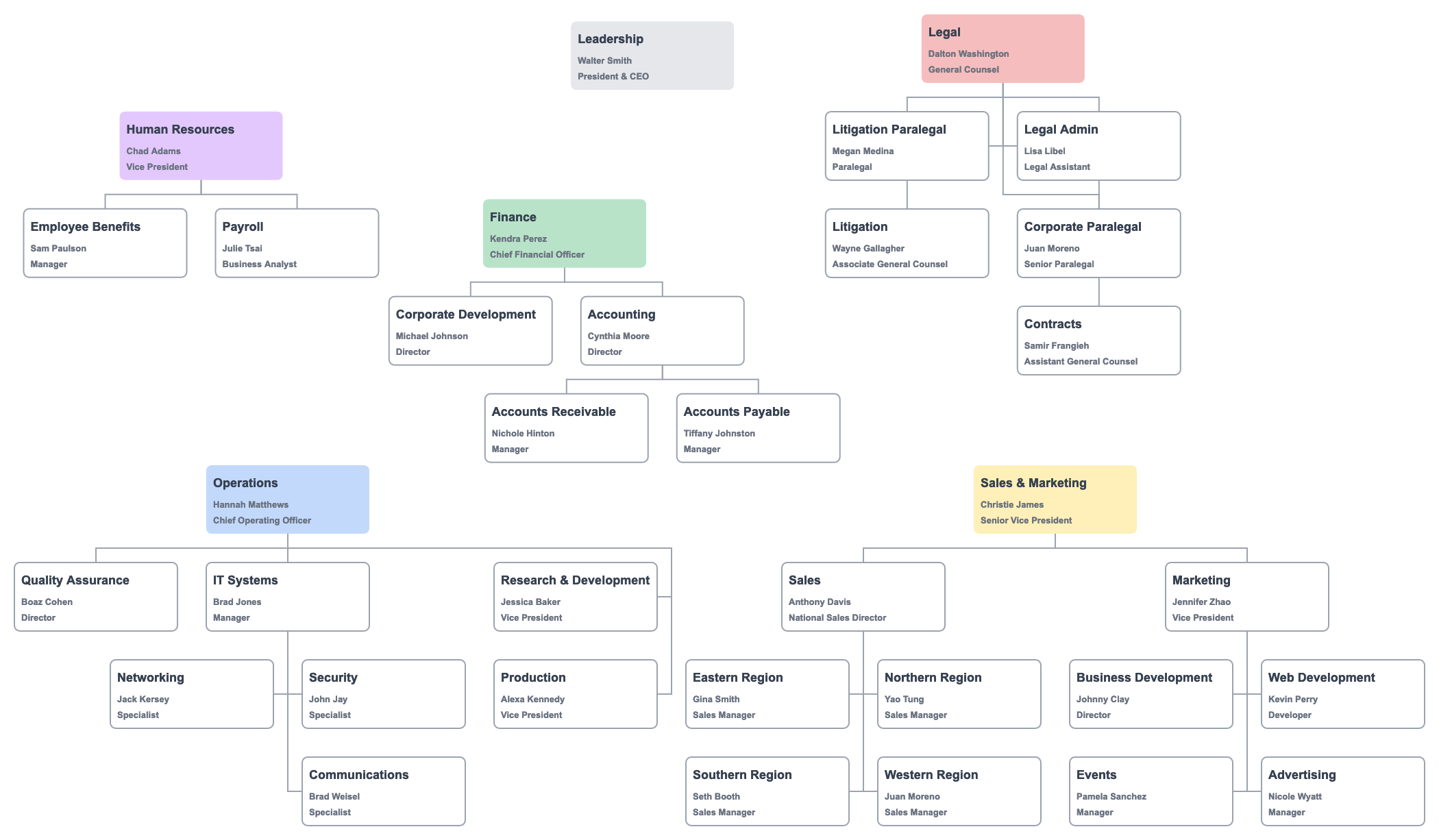
Depending on the size of the organization, a functional chart might focus on the general department structure or a particular department.
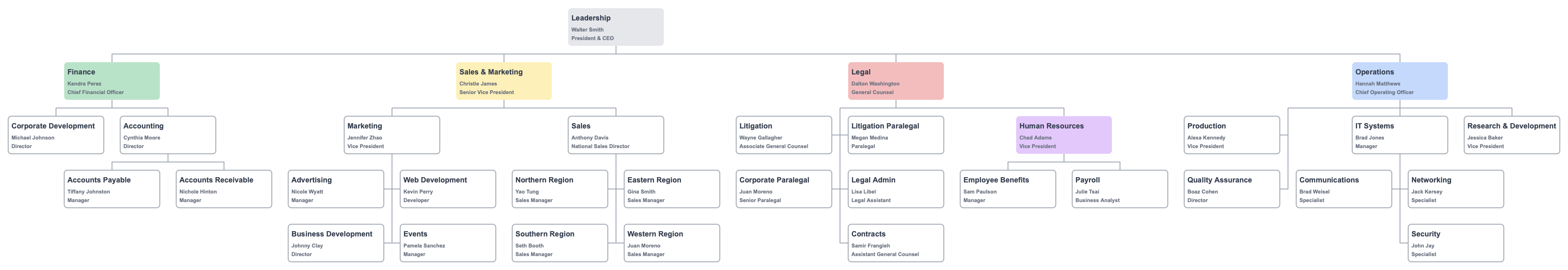
A focus on a few departments might look like this:
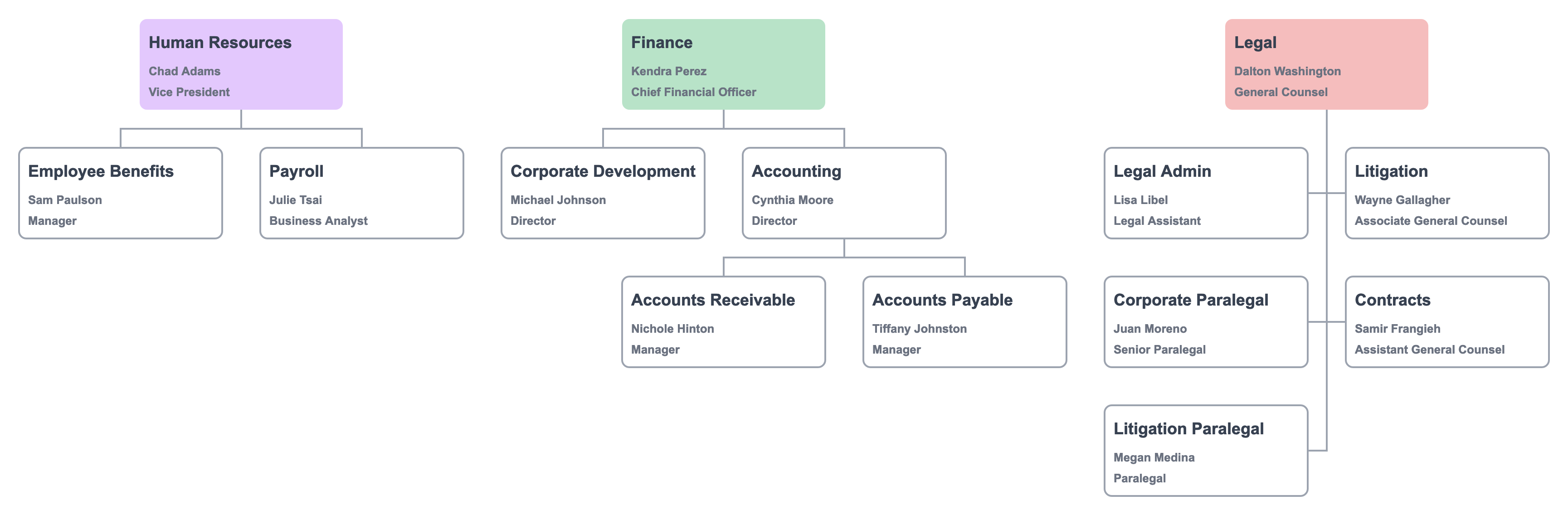
Org chart after reorganization
Organizational structures are not permanent. Org chart software allows organization design professionals to model changes in the structure.
In a functional org chart, you might have one department report to another department. A reorganization that has, for example, Human Resources report to Legal might look like this:
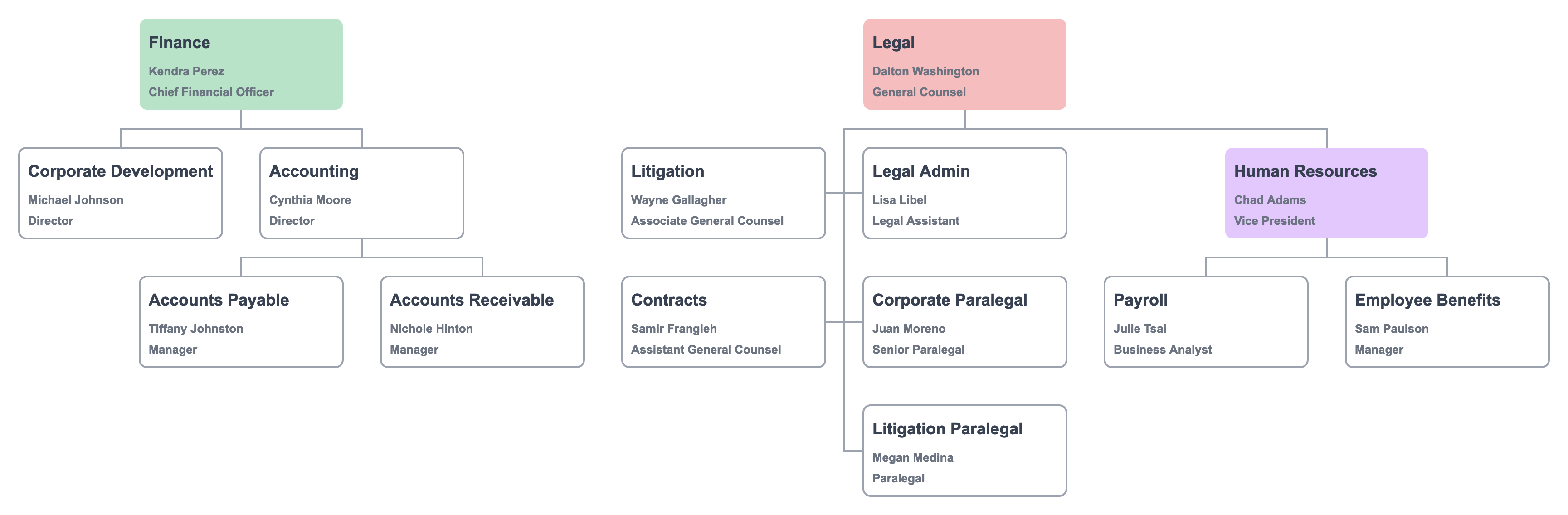
In Lexchart, those changes are simple.
Matrix organizational structure
A matrix organizational structure attempts to combine a functional structure with a team structure. Staff have direct reporting relationships to functional managers. Staff then have a second reporting relationship to a project manager that crosses functional silos.
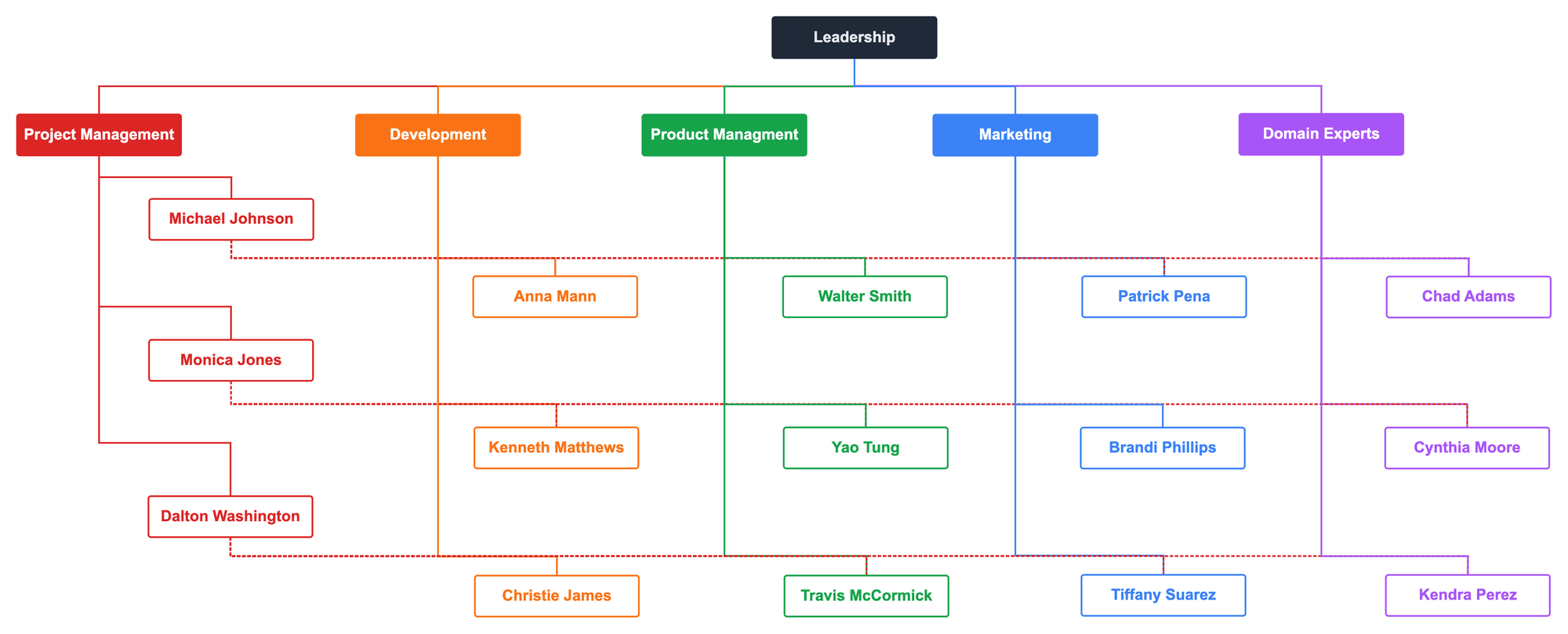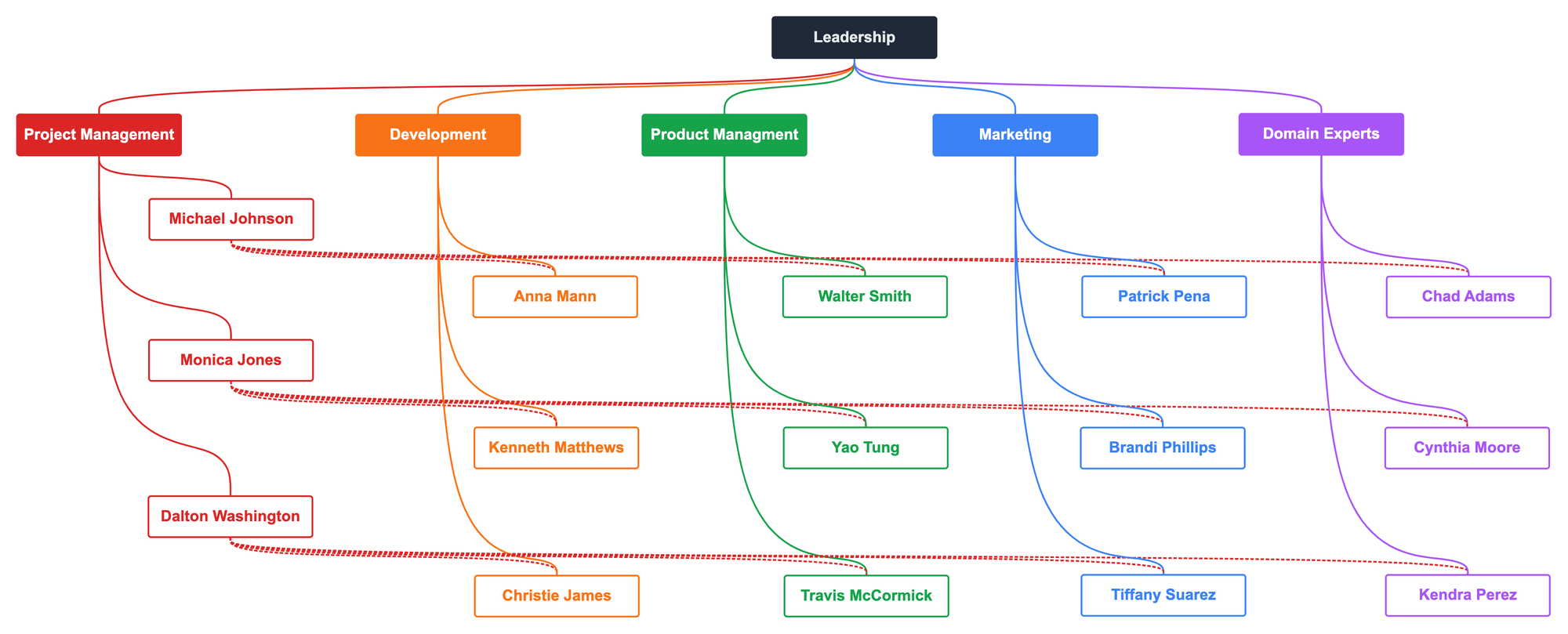
This image of a matrix structure alternates between elbow and curved connectors to distinguish the dual reporting lines for each staff member.
There are three variations of a matrix organizational structure:
- Weak matrix structure,
- Balanced matrix structure, and
- Strong matrix structure.
Each variation attempts to resolve the tension created by having two managers. Who has responsibility over the project?
Weak matrix structure
In a weak matrix structure, decision making over the project rests with the functional manager. The problem is that each functional manager can then work at cross purposes to the project.
Balanced matrix structure
The theory behind a balanced matrix structure is that the functional and project managers have an equal say in the project.
Strong matrix structure
A strong matrix structure assigns primary responsibility and authority over the project to the project manager. For a strong matrix structure org chart, you might make the lines between the project manager and team members solid; the lines between the functional managers and team members dotted.
Conclusion
While no two functional organization structures are identical, as an approach to diagramming organization structure, a functional org chart is an excellent choice.
If you need to know how to create an org chart or present an org chart, check out the Complete Guide to Organization Charts.
All names and roles are fictional. ↩︎

