Limited Liability Company structure
There are four types of limited liability companies in the United States:
- Sole member LLC,
- Member managed LLC,
- Manager managed LLC, and
- Series LLC.
This article focuses on the first three.
Limited liability company principles
LLCs can have any number of members. An LLC member is an owner of the business. An LLC member is analogous to a shareholder of a corporation and a partner in a partnership.
Membership in an LLC comes with a bundle of financial and management (voting) interests which can be separated and parceled out among members.
Limited liabilities companies enjoy pass through tax status, similar to partnerships, although they can elect different tax treatment.
LLC operating agreements are diverse, ranging from the simple to the byzantine. The business strategy, capital raising, and investment objectives shape the operating agreement.
Member managed LLCs
A member managed limited liability company is an LLC where the owners of the business (members) also manage the operations of the business.
This video shows a member managed LLC where the members have different voting and financial interests.
Sole member LLCs and member managed LLCs
A sole member LLC is a type of member managed LLC. In both cases, the ownership interests and management responsibilities rest with the same person or persons. While the members of sole and manager managed LLCs are often natural persons, they can be other legal entities.
This video compares the structure of a sole member LLC to a multi-member LLC where the members serve as managers.
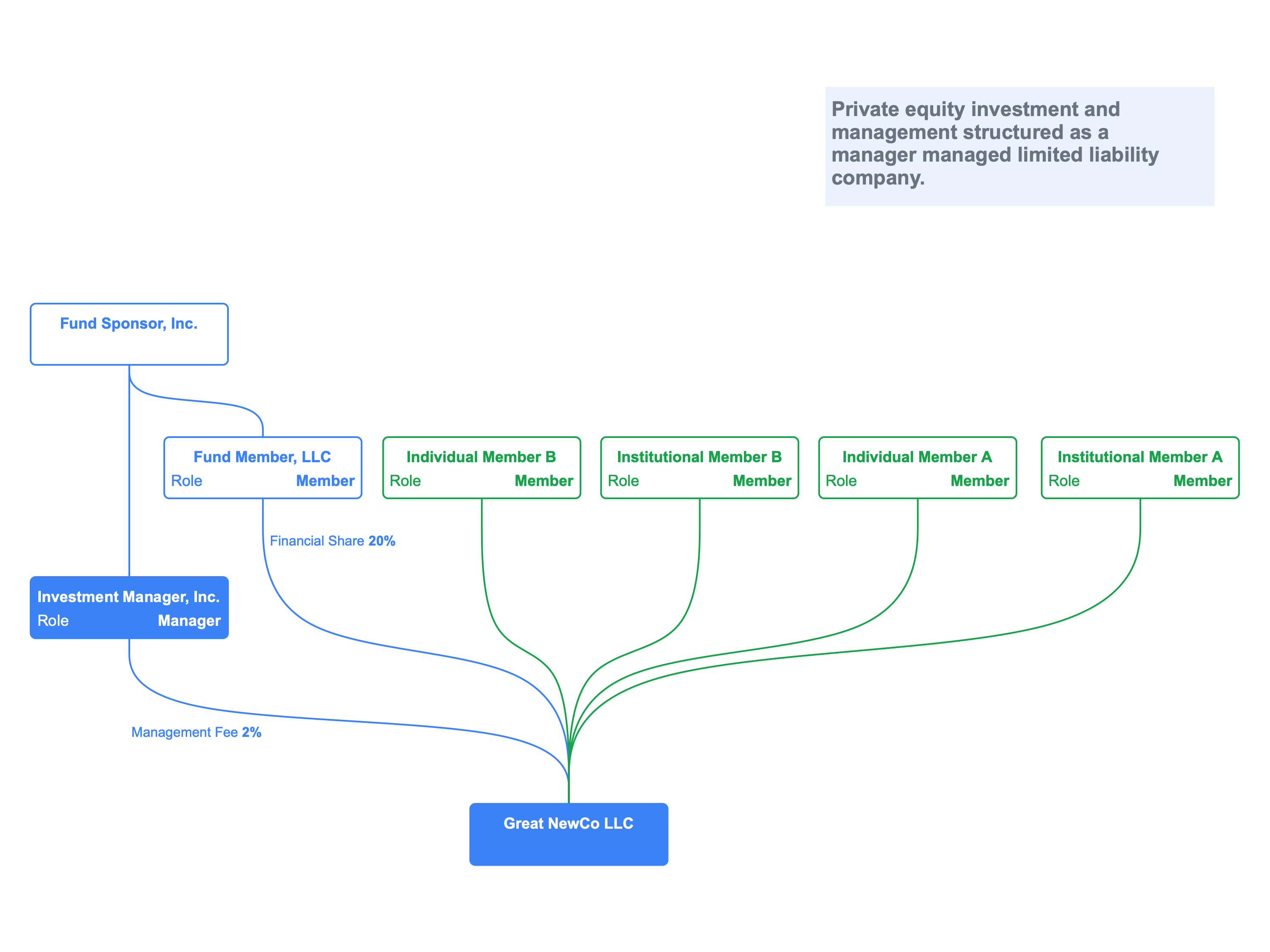
Manager managed LLCs
A manager managed limited liability company is an LLC where the management of the business is separate from the ownership of the business.
Members can, however, serve as managers provided the operating agreement delineates the roles and responsibilities.
This video shows the transformation of a manager managed LLC with an independent manager to one where a member becomes one of the managers.
The manager or managers of a manager managed LLC may be a natural person or a legal entity. An LLC could, for example, look like a private equity limited partnership.
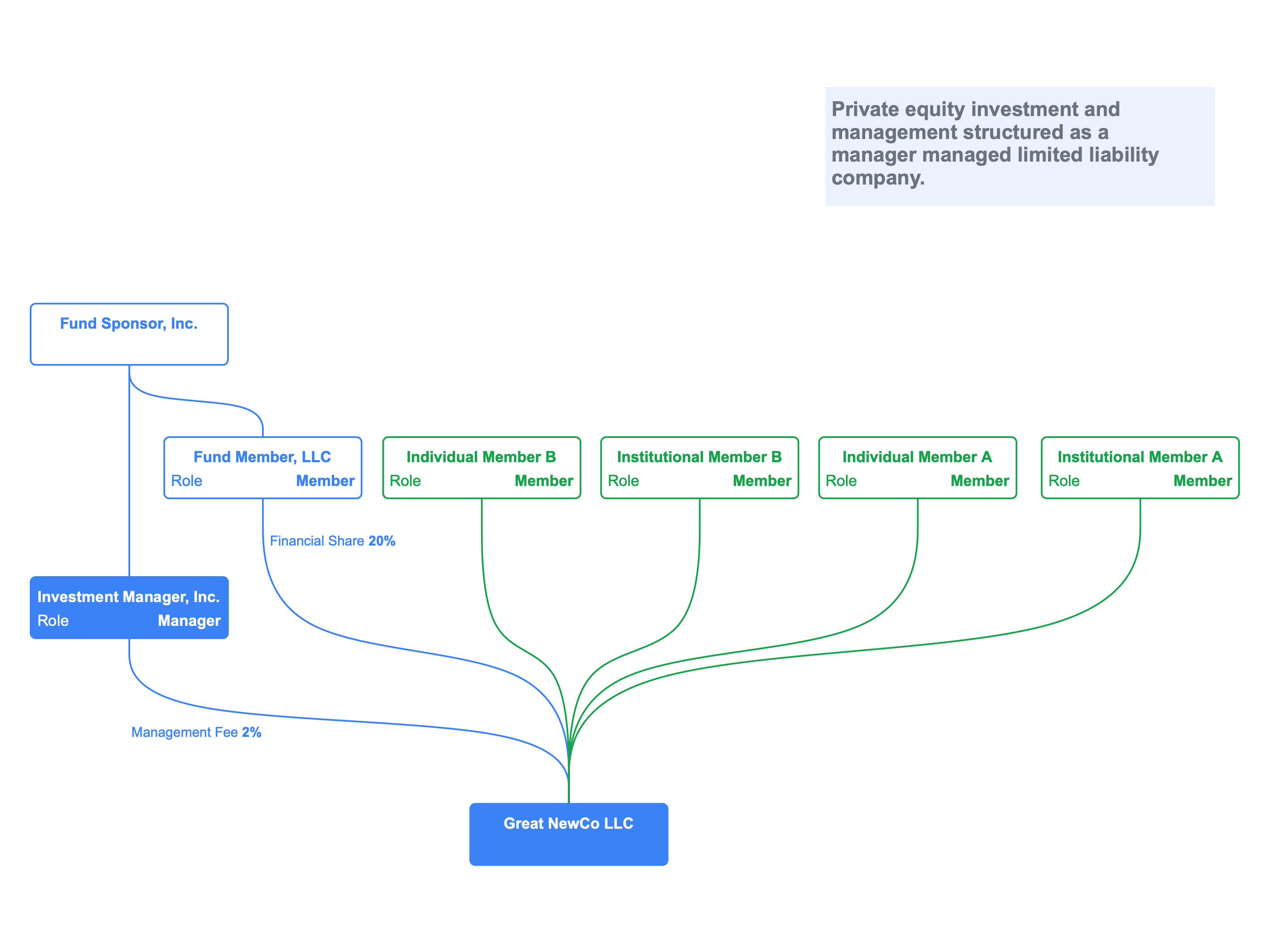
Conclusion
Limited liability company structures are diverse and flexible. The organizational flexibility combined with pass through tax status explains the explosive growth of the LLC legal entity structure.

